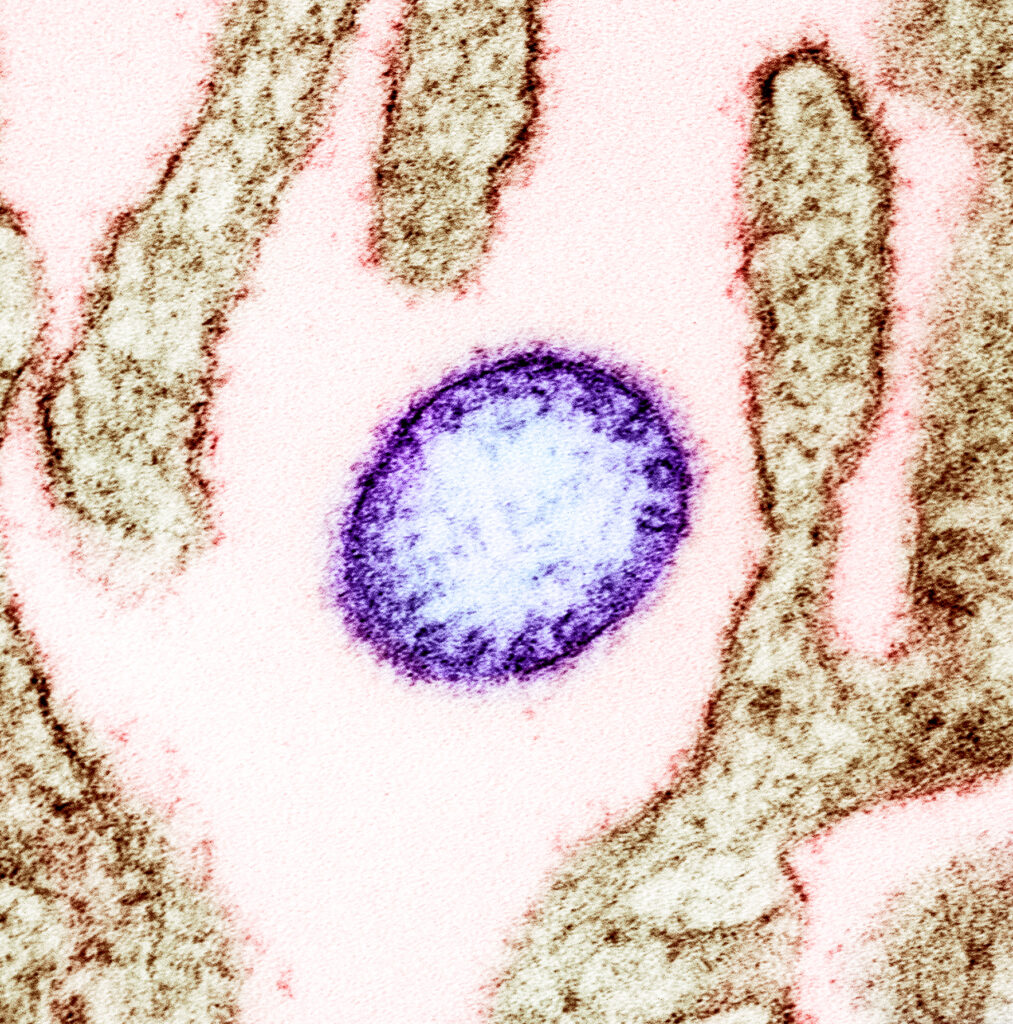
Nipah virus is a bat-borne, zoonotic virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a very high mortality rate (40-75%). Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in North East Africa and Southeast Asia. Nipah virus belongs to the genus Henipavirus along with the Hendra virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks.
TRANSMISSION
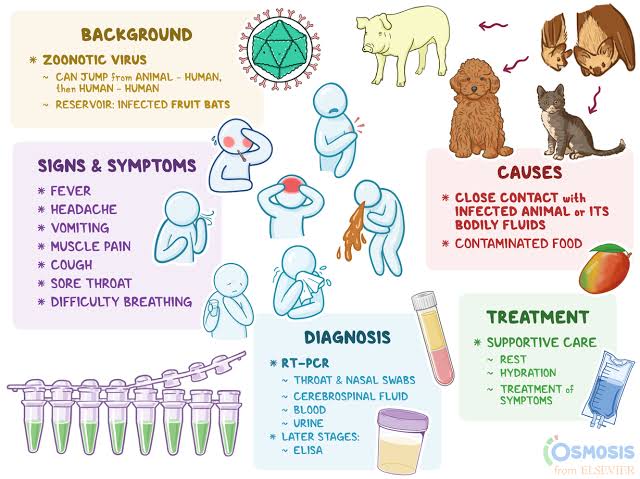
Nipah virus can spread to people from:
- Direct contact with infected animals, such as bats and pigs, or their body fluids( such as blood, urine or saliva)
- Consuming food products that have been contaminated with body fluids of infected animals (such as palm sap or fruit contaminated by an infected bat)
- Close contact with a person infected with NiV or their body fluids ( including nasal or respiratory droplets, urine or blood)
SYMPTOMS
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Vomiting
- Sore throat
These symptoms can be followed by more serious conditions including:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Altered consciousness
- Acute encephalitis
- Atypical pneumonia
- Severe respiratory distress
- Seizures
DIAGNOSIS
During early stages of the illness, laboratory testing can be conducted using real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from throat and nasal swabs, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and blood. Later in the course of illness and after recovery, testing for antibodies is conducted using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA).
TREATMENT
Treatment is limited to supportive care, including rest, hydration, and treatment of symptoms as they occur. There are, however, immunotherapeutic treatments (monoclonal antibody therapies) that are currently under development and evaluation for treatment of NiV infections.