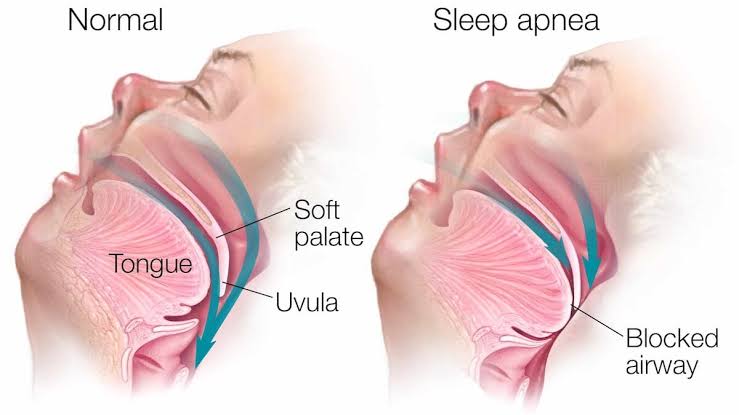
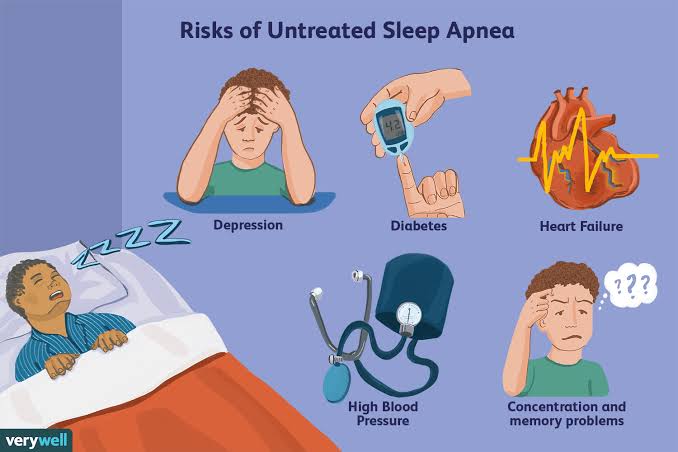
Sleep apnea is a serious sleeping disorder characterized by an interruption in breathing or shallow breathing while an individual is asleep. Each interruption can happen many times during night and may take a few seconds to a few minutes. It is common among adults and becoming more common in children. If left untreated, it can lead to serious disorders such as high blood pressure, diabetes and stroke.
Types:
There are three types of sleep apnea:
· Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep apnea and is caused by obstruction of airways usually when throat muscle relaxes. People of any age can be affected. However, it is more common in adults usually of age between 55 to 60 years old.
· Central sleep apnea (CSA) happens when the brain fails to transmit signals to muscles that control breathing. It affects less than 1% of people.
· Mixed sleep apnea (MSA) occurs when an individual has both central and obstructive sleep apnea.
Causes:
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the back of your throat relax causing a blocked airway. There are factors that can predispose an individual to this form of sleep apnea. This factor includes:
· Smoking
· Nasal congestion
· Narrowed airway
· Obesity
· Aging
· Family history
· Use of alcohol or sedatives
Central sleep apnea occurs when the brain’s area that controls breathing fails to send signals to the breathing muscles. Factors that can predispose a person to this type of sleep apnea are:
· Aging
· Stroke
· Heart disorders
· Use of narcotics
Symptoms:
· Loud snoring
· Morning headaches
· Attention problems
· Excessive daytime sleepiness or fatigue
· Insomnia
· Awakening with a dry mouth or sore throat
· Episodes of breathing cessation
· Awakening at night accompanied by shortness of breath

Diagnosis:
Sleep apnea can be diagnosed by the assessment of symptoms and risk factors. Such assessment may involve overnight monitoring of your sleeping and other body activities while sleeping. The standard test for sleep apnea is polysomnography, also known as sleep test. During Polysomnography, you’re observed overnight while connected to many sensors. During this study, the following information is recorded.
· Sleep stages
· Heart rate
· Body oxygen level
· Muscle activity
· Waves and breathing rate
· Eye movement
· Audio recording of loudness of snoring
For some, a home sleep apnea test (HSAT) can be done. The severity of sleep apnea is determined by the episodes of apnea per hour.
· For normal, 0-5 apnea episodes per hour
· For mild, 5-15 episodes per hour
· For moderate, 16-30 episodes per hour
· For severe, more than 31 episodes per hour
If you have sleep apnea, an ENT specialist doctor may have to test you to rule out any blockage in your nose or throat.
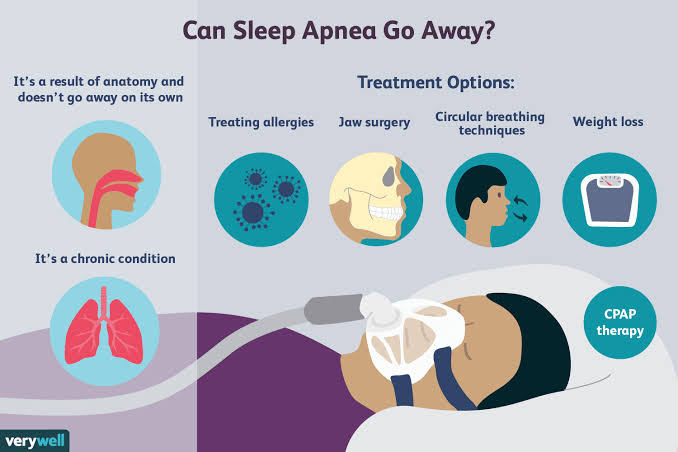
Treatment:
For less severe sleep apnea, your doctor may suggest some lifestyle changes such as smoking cessation, losing weight and treating your nasal congestion. If these measures don’t improve your symptoms, a number of other available treatments can be used. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), oral appliances or expiratory positive airway pressure (EPAP) can all be used to open blocked airways. Surgery may be recommended after all treatments have failed. Surgical options may include tissue removal, implants, jaw reposition or creating a new passage way.
For central and mixed sleep apnea, treatment may include:
· Supplemental oxygen
· Adaptive servo ventilation
· Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
· Bilevel positive airway pressure