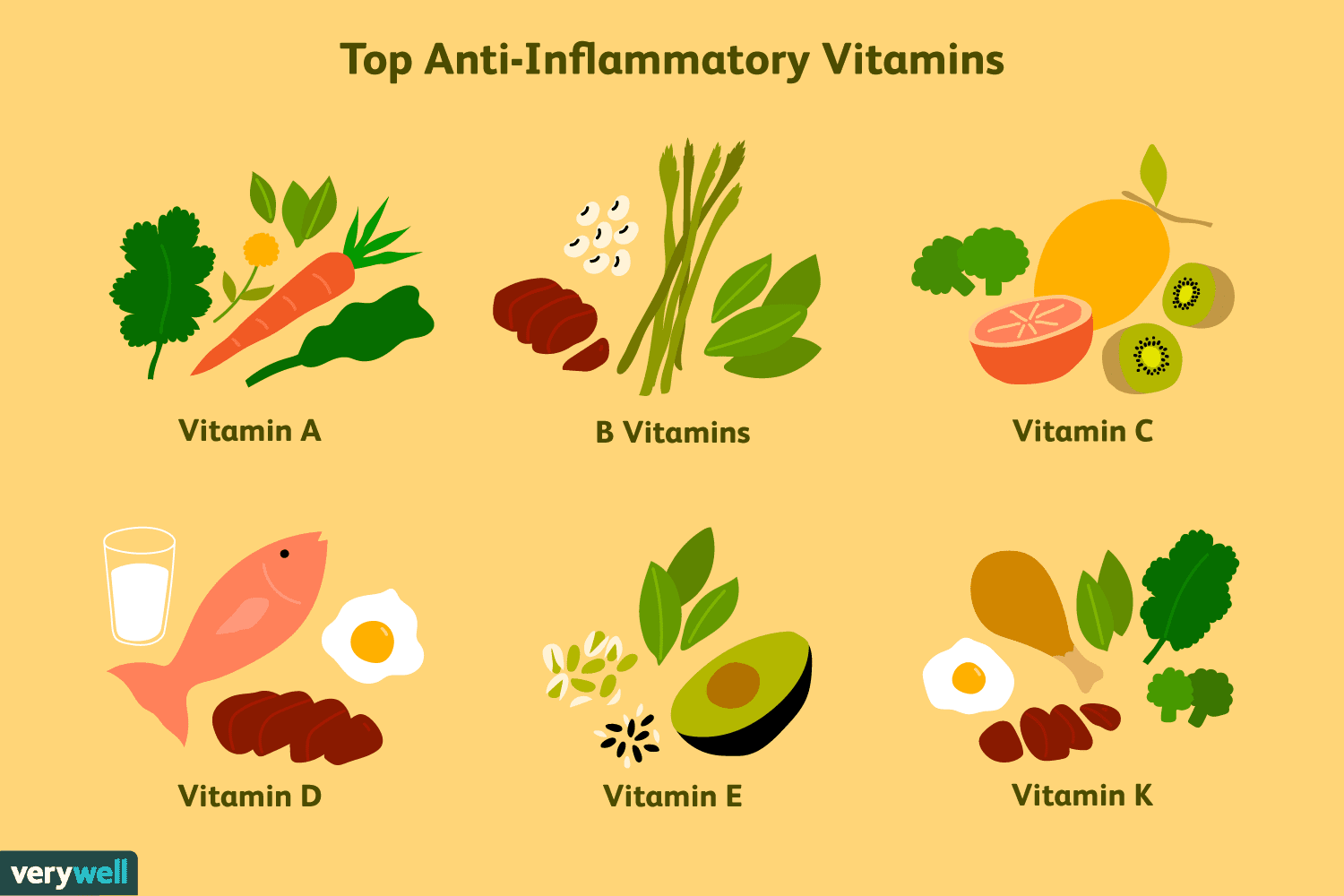
Vitamins
Vitamins are the chemical compounds that are required in low amounts but are essential for normal growth and metabolism. Vitamins may be divided into two groups: the fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A,D,E and K) and the water-soluble vitamins (vitamin B and vitamin C).
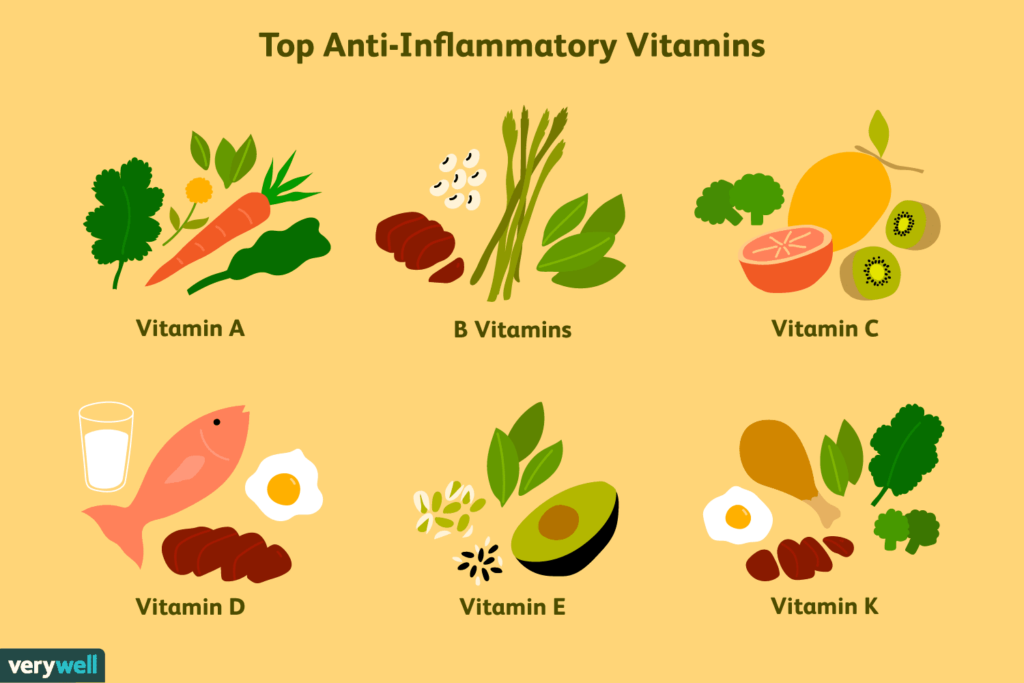
Vitamin A
Vitamin A was the first fat-soluble vitamin identified (in 1913). It combines with a protein called opsin to form rhodopsin in rod cells of the retina of eye. When vitamin A is inadequate, the lack of rhodopsin makes it difficult to see in dim light. It is also involved in cell differentiation, a process through which embryonic cells transform into mature cells, with specific functions. Vitamin A also supports bone growth and immune functions.
Humans get vitamin A from leafy vegetables (spinach, carrots), yellow/orange fruits (mango), liver, fish, egg, milk, butter etc. Deficiency of vitamin A is the leading cause of blindness in children worldwide. One of the symptoms of vitamin-A deficiency in night blindness. It is a temporary condition, but if left untreated it can cause permanent blindness. Vitamin-A deficiency can also cause a condition in which hair follicles become plugged with keratin, giving dry texture to skin.
Vitamin C ;(Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamins C participates in many reactions. It is needed to form collagen (a fibrous protein) that gives strength to connective tissues. Collagen is also needed for the healing of wounds. Vitamin C in white blood cells enables the immune system to function properly.
We get vitamin C from citrus fruits (e.g. oranges, lemons, and grape fruit), leafy green vegetables, beef liver etc. Deficiency of vitamin C causes connective tissue changes throughout the body. The disease known as scurvy results from lack of vitamin C. In this condition the synthesized collagen is unstable. Symptoms of scurvy include muscle and joint pain. Swollen and bleeding gums, slow wounds healing, and dry skin.
Vitamin D
The best-known function of vitamin D is to help regulate blood levels of calcium and phosphorous. Vitamin D increases the absorption of these minerals from intestine and their deposition in bones.
Vitamin D is mainly found in fish liver oil, milk, ghee, and butter etc. It is also synthesized by skin when ultraviolet (UV) radiations from the sun are used to convert a compound into vitamin D. Long-term deficiency of vitamin D affects bones. It children, vitamin-D deficiency leads to rickets a condition in which bones weaken bow under pressure. In adults, vitamin-D deficiency causes osteomalacia, “softening bones”, increasing the risk for fractures in bones.