What is the most common presentation of a heart attack? Heart attacks often present as sudden death, historically being the most common initial sign, emphasizing the critical need for preventive measures.
Three factors to look after to prevent heart attack are;
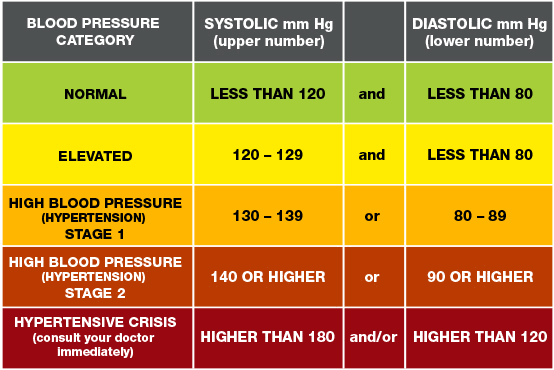
· Blood pressure
· Smoking
· ApoB levels
Exercise, weight management, and lifestyle changes are prioritized to manage blood pressure before turning to medications, aiming to minimize medication’s side effects. Quality sleep, exercise (especially low-intensity cardio), and nutrition play pivotal roles in heart health before resorting to pharmacotherapy. Blood pressure’s impact on the kidneys is often overlooked; monitoring kidney function is crucial as compromised kidney health significantly affects longevity and mortality risk.
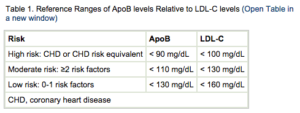
Apolipoprotein B-100 Test helps your doctor analyze whether or not you’re at risk for heart disease. It measures the amount of Apolipoprotein B in your blood. Apolipoprotein B attaches to negative types of cholesterol that causes plaque buildup in your blood vessels, which can lead to damage and cause heart disease. The ApoB test is a simple blood test. A lab technician or nurse draws blood from your arm to use for analysis. The normal range for Apolipoprotein B is less than 90 mg/dL, of blood. ApoB measurements for assessing heart attack risk should ideally start in the 20s or 30s, especially with a family history of heart issues.
Getting physically active improves lipid management, including lowering your ApoB. Regular exercise allows you to use more energy, which may utilize stored glucose in fat(glycogen). This can significantly reduce fat accumulation over time.
Taking garlic as your daily routine diet. A 2022 scientific review published in the frontiers in Pharmacology has shown that garlic possesses anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic (ability to lower lipoproteins), and antiatherogenic (inhibiting plaque formation) properties. These make garlic an ideal supplement for people at risk of cardiovascular disease, including those with high ApoB.